教育经历
-
 中国科学技术大学近代力学系
中国科学技术大学近代力学系
流体力学博士研究生2023年9月至今 -
 中国科学技术大学近代力学系
中国科学技术大学近代力学系
流体力学硕士研究生2021年9月至2023年6月 -
 中国科学技术大学本科,理论与应用力学2017年9月至2021年6月
中国科学技术大学本科,理论与应用力学2017年9月至2021年6月 -
 哈尔滨市第三中学校高中生2014年9月至2017年6月
哈尔滨市第三中学校高中生2014年9月至2017年6月
工作经历
-
 香港理工大学研究助理2024年10月至2025年5月
香港理工大学研究助理2024年10月至2025年5月 -
 中国科学技术大学助教(流体力学基础、气体动力学基础)2020年9月至2021年6月
中国科学技术大学助教(流体力学基础、气体动力学基础)2020年9月至2021年6月
荣誉及奖项
-
中国科协青年科技人才培育工程博士生专项计划2025
-
博士生国家奖学金2025
-
第21届全国激波与激波管学术会议优秀论文奖2024
-
研究生一等学业奖学金2021, 2022, 2024, 2025
-
研究生二等学业奖学金2023
-
气体动力学基础(英)课程优秀助教2021
发表论文
- Jiaxuan Li, Qing Cao, He Wang, Zhigang Zhai, Xisheng Luo. New interface formation method for shock–interface interaction studies, Exp. Fluids, 64(11): 170, 2023
- Jiaxuan Li, Zhigang Zhai. Modelling and mechanism of non-standard Richtmyer-Meshkov instability at a heavy-light interface. J. Fluid Mech., 1023, A6, 2025.
- Jiaxuan Li, Chenren Chen, Zhigang Zhai, Xisheng Luo. Asymptotic matching modal theory and experiments on Richtmyer-Meshkov instability. J. Fluid Mech., 1002, A16, 2025
- Jiaxuan Li, Chenren Chen, Zhigang Zhai, Xisheng Luo. Effects of compressibility on Richtmyer-Meshkov instability of heavy/light interface. Phys. Fluids, 36, 056104, 2024
- Jiaxuan Li, He Wang, Zhigang Zhai, Xisheng Luo. Richtmyer–Meshkov instability of a single-mode heavy–light interface in cylindrical geometry, Phys. Fluids, 35, 106112, 2023
- Qing Cao, Jiaxuan Li, He Wang, Zhigang Zhai, Xisheng Luo. Coupled Richtmyer–Meshkov and Kelvin–Helmholtz instability on a shock-accelerated inclined single-mode interface, J. Fluid. Mech., 996, A37, 2024
- Chenren Chen, Jiaxuan Li, Zhigang Zhai. Atwood-number dependence of the instability evolution at a shock-accelerated heavy fluid layer, J. Fluid Mech., 1027, A13, 2026
- Chenren Chen, Jiaxuan Li, He Wang, Zhigang Zhai, Xisheng Luo. Effects of disturbed transmitted shock and interface coupling on heavy gas layer evolution, Phys. Fluids, 36, 086108, 2024
- Chenren Chen, Jiaxuan Li, He Wang, Zhigang Zhai, and Xisheng Luo. Attenuation of Richtmyer-Meshkov instability growth of fluid layer via double shock, Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 68, 244711, 2025
- Yinuo Xing, Chenren Chen, Jiaxuan Li, He Wang, Zhigang Zhai, and Xisheng Luo. Atwood-number dependence of the Richtmyer-Meshkov instability at a heavy-light single-mode interface, J. Fluid Mech. 1007, A54, 2025
- Zhigang Zhai, Chenren Chen, Yinuo Xing, Jiaxuan Li, Qing Cao, He Wang, and Xisheng Luo. Manipulation of Richtmyer-Meshkov instability on a heavy-light interface via successive shocks, J. Fluid. Mech., 1003, A9, 2025
精选工作 (view all )

Modelling and mechanism of non-standard Richtmyer-Meshkov instability at heavy-light interfaces under moderate Mach numbers
J. Fluid Mech. 2025 Newest-work
This study presents an analytical advancement in predicting the growth rate of perturbation amplitude in two-dimensional non-standard Richtmyer-Meshkov instability (RMI), driven by the interaction of a first-phase rippled shock wave at moderate Mach number with a heavy-light interface. We extend the irrotational model to encompass non-standard RMI scenarios, establishing a generalized framework validated through numerical simulations. Distinct from previous models, our model is free of empirical coefficients, and demonstrates superior accuracy across diverse perturbation configurations and Mach numbers. The analyses reveal the fundamental disparity of non-standard RMI from classical RMI: the vorticity deposition mechanism in non-standard RMI arises not only from normal pressure gradients at the shock front but crucially from tangential pressure gradients behind the shock wave. The asymptotic circulations are also well predicted by our model. Moreover, the relationship of the amplitudes between sinusoidal shock and perturbed interface is derived based on the model to realize the freeze-out of interface amplitude. The initial fundamental mode's amplitude growth is frozen well, and the mixing width is greatly suppressed.
Modelling and mechanism of non-standard Richtmyer-Meshkov instability at heavy-light interfaces under moderate Mach numbers
J. Fluid Mech. 2025 Newest-work
This study presents an analytical advancement in predicting the growth rate of perturbation amplitude in two-dimensional non-standard Richtmyer-Meshkov instability (RMI), driven by the interaction of a first-phase rippled shock wave at moderate Mach number with a heavy-light interface. We extend the irrotational model to encompass non-standard RMI scenarios, establishing a generalized framework validated through numerical simulations. Distinct from previous models, our model is free of empirical coefficients, and demonstrates superior accuracy across diverse perturbation configurations and Mach numbers. The analyses reveal the fundamental disparity of non-standard RMI from classical RMI: the vorticity deposition mechanism in non-standard RMI arises not only from normal pressure gradients at the shock front but crucially from tangential pressure gradients behind the shock wave. The asymptotic circulations are also well predicted by our model. Moreover, the relationship of the amplitudes between sinusoidal shock and perturbed interface is derived based on the model to realize the freeze-out of interface amplitude. The initial fundamental mode's amplitude growth is frozen well, and the mixing width is greatly suppressed.

Asymptotic matching modal model on Richtmyer–Meshkov instability
Jiaxuan Li, Chenren Chen, Zhigang Zhai, Xisheng Luo
J. Fluid Mech. 2025 Spotlight
An asymptotic matching modal model is established based on the singular perturbation method for predicting mode evolution in single- and dual-mode interfaces accelerated by a shock wave. The startup process is incorporated into the model to provide a complete description of the mode evolution after the shock impact. Through considering the feedback from high-order harmonic to the third-order harmonic, the model accuracy is improved and the model divergence is prevented. In addition, the model can evaluate the mutual-coupling effect on the amplitude variations of high-order harmonics besides the ‘beat modes’. To validate the model, experiments on both light–heavy and heavy–light interfaces subject to a shock wave are conducted, and both single- and dual-mode interfaces formed by the soap-film technique are involved. The interface profiles extracted from mode decomposition and predicted by the model show high consistency with the experimental counterparts. Good agreement of the mode amplitude growths between the experiments and theoretical predictions shows the superiority of the model, especially for the heavy–light interface.
Asymptotic matching modal model on Richtmyer–Meshkov instability
Jiaxuan Li, Chenren Chen, Zhigang Zhai, Xisheng Luo
J. Fluid Mech. 2025 Spotlight
An asymptotic matching modal model is established based on the singular perturbation method for predicting mode evolution in single- and dual-mode interfaces accelerated by a shock wave. The startup process is incorporated into the model to provide a complete description of the mode evolution after the shock impact. Through considering the feedback from high-order harmonic to the third-order harmonic, the model accuracy is improved and the model divergence is prevented. In addition, the model can evaluate the mutual-coupling effect on the amplitude variations of high-order harmonics besides the ‘beat modes’. To validate the model, experiments on both light–heavy and heavy–light interfaces subject to a shock wave are conducted, and both single- and dual-mode interfaces formed by the soap-film technique are involved. The interface profiles extracted from mode decomposition and predicted by the model show high consistency with the experimental counterparts. Good agreement of the mode amplitude growths between the experiments and theoretical predictions shows the superiority of the model, especially for the heavy–light interface.
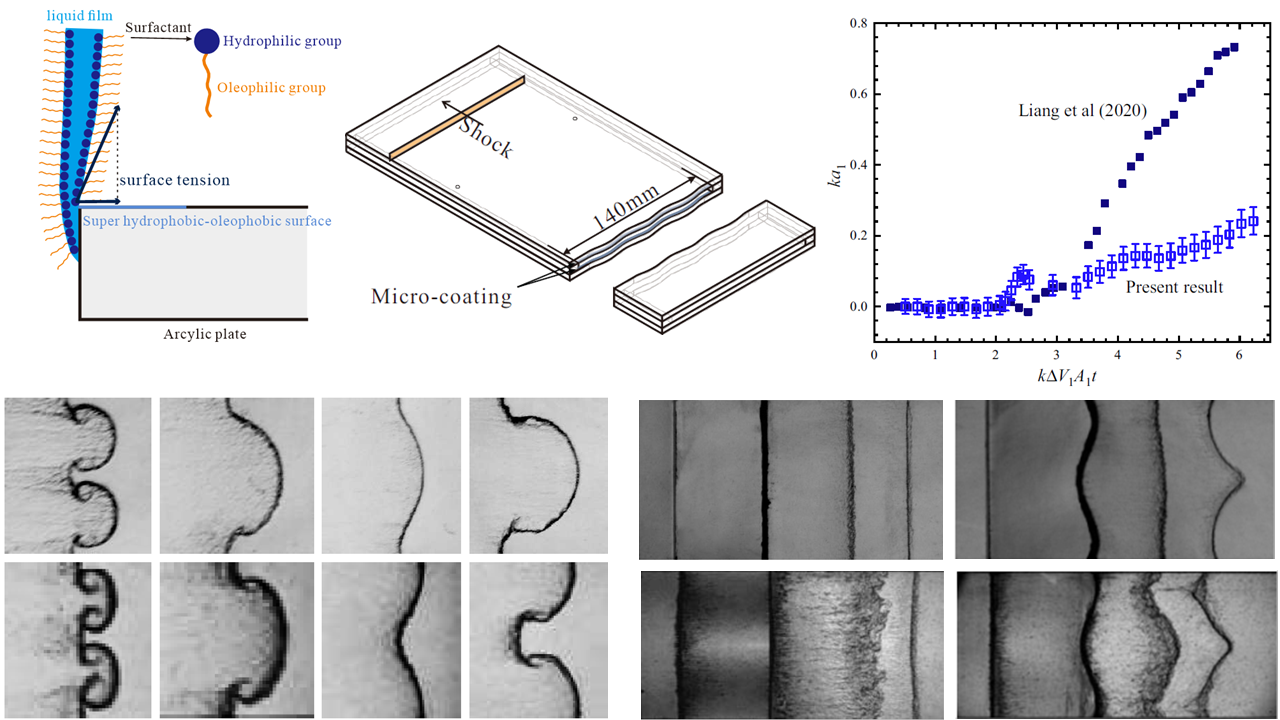
New interface formation method for shock–interface interaction studies
Jiaxuan Li, Qing Cao, He Wang, Zhigang Zhai, Xisheng Luo
Exp. Fluids 2023 My-Favorite-Work
We propose a new interface formation method for shock–interface interaction studies by using the super-hydrophobic–oleophobic surface instead of filaments to constrain the soap–film interface. To verify this method, developments of a single-mode air–SFinterface and a heavy gas layer accelerated by shock waves are experimentally investigated and compared with the previous studies. For single-mode interface developments, experimental schlieren images show that the interfaces are more fully developed, and the thickness of the interface profile reduces more than 60%. For shock-induced heavy gas layer instability, the interface profile is more distinct, and the mixing width of the upstream interface after it passes through the initial position of the downstream interface is largely weakened. Quantitative comparison shows that the filaments used to constrain the soap–film interface have a significant effect on the movement and amplitude growth of the upstream interface, and the superiority of the present method is well demonstrated.
New interface formation method for shock–interface interaction studies
Jiaxuan Li, Qing Cao, He Wang, Zhigang Zhai, Xisheng Luo
Exp. Fluids 2023 My-Favorite-Work
We propose a new interface formation method for shock–interface interaction studies by using the super-hydrophobic–oleophobic surface instead of filaments to constrain the soap–film interface. To verify this method, developments of a single-mode air–SFinterface and a heavy gas layer accelerated by shock waves are experimentally investigated and compared with the previous studies. For single-mode interface developments, experimental schlieren images show that the interfaces are more fully developed, and the thickness of the interface profile reduces more than 60%. For shock-induced heavy gas layer instability, the interface profile is more distinct, and the mixing width of the upstream interface after it passes through the initial position of the downstream interface is largely weakened. Quantitative comparison shows that the filaments used to constrain the soap–film interface have a significant effect on the movement and amplitude growth of the upstream interface, and the superiority of the present method is well demonstrated.

